AVAILABLE NOW!
1.7227+QT is already available, but not yet listed in the online shop.
Please contact us for prices and dimensions.
☎️ +44 (0) 121 368 0910


1.7227 +QT - AT A GLANCE
What kind of steel is the 1.7225 +QT?
As a low alloyed steel does the 1.7227+QT (here in its tempered condition) need the alloyed chromium and molybdenum to elevate its strength and hardenability. The added sulphur gives this steel grade a better machinability. Its chromium content makes sure that this heat treatable steel can be hardened through while the added molybdenum offers an even strength and hardness.
The combination of mechanical properties and the machinability make this steel grade a good choice for many applications in many industries.
Properties
Heat treatable steel 1.7227+QT also known as the 42CrMoS4+QT is a low alloyed chromium-molybdenum-steel. This steel grade is characterised by its high strength, good toughness and hardenability. It can be used for machine and tool construction and many other industries due to the former meantioned properties.
- Excellent wear resistance
- Excellent stress resistance
- Improved machinability
- High hardness
- High toughness
- Nitridable
- EMD machinable
- Difficult to weld
Applications
The 1.7227+QT is due to its high hardness and high toughness very versatile.
Heat treatable steel 1.7227+QT can be used for the following applications:
- Mandrels
- Flanges
- Collets
- Bending dies
- Crankshafts
- Clutch parts
- Forming rolls
- Short run stamping dies
- Mechanical engineering
- Machine parts
- Axes
- Knuckles
- Connecting rods
- Crankshafts
- Gear shafts
- Pinions
- Gears
- Bandages
- Base plates
- Assembling parts
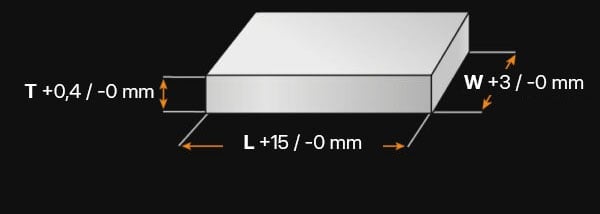
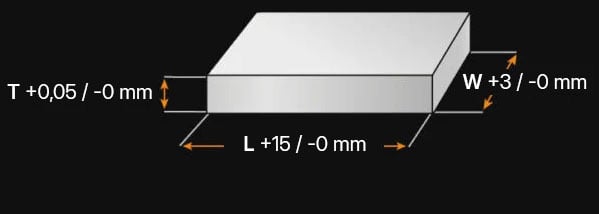
1.7227+QT Standard values
Chemical composition:
| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Mo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.38 - 0.45 | 0.0 - 0.4 | 0.6 - 0.9 | 0.0 - 0.035 | 0.02 - 0.04 | 0.9 - 1.2 | 0.15 - 0.3 |
Chemical designation:
42CrMoS4+QT
Working hardness:
max. 48 HRC
Delivery condition:
max. 270 HB, tempered
1.7227+QT Physical properties
What group of steel does the 1.7227+QT belong to?
- Heat-treatable steel
- Cold work steel
Is the 1.7227+QT a stainless steel?
Even with a chromium and molbdenum content the 1.7227+QT is not a classic stainless steel as the classic 10,5% chromium stainless steel- It belongs to the group of high quality structural steel.
Is the 1.7227+QT corrosion resistant?
No the 1.7227+QT is not corrosion resistant. To be classified as a stainless steel the grade has to have a chromium content of at least 10,5 %. The 1.7227+QT has only got a massfraction of 0,9 – 1,2 % of chromium.
Is the 1.7227+QT magnetisable?
The heat-treatable steel 1.7227+QT is magnetisable and magnetic clamping can be used for machining, milling and grinding for example.
1.7227+QT Wear resistance
On a scale where 1 is low and 6 is high the 1.7227+QT receives a 3 for its wear resistance.
1.7227+QT Technical properties
Is the 1.7227+QT a knife steel?
When producing a knife with the 1.7227+QT corrosion resistance, hardness as well as wear resistance should be a focus. Though it is possible to make a knife with this material gade it is not usually used to manufacture knives.
1.7227+QT Working hardness
The working hardness for the 1.7227+QT is in the range of 27 – 48 HRC.
1.7227+QT Density
At room temperature the density for the 1.727+QT is at ,85 g/cm3.
1.7227+QT Tensile strength
The tensile strength for the 1.7227+QT is at max. 900 N/mm2. The tensile strength indicates the maximum load capacity. To obtain this information, a tensile test is carried out to determine how much force is required to elongate or stretch a sample before it breaks.
1.7227+QT machinability
On a scale the 1.7227+QT receives a 5 for its machinabilty on a scale where 1 is low and 6 is high.
1.7227+QT Yield strength
The yield strength for the 1.7227+QT is at approx.655 N/mm2. It indicates how much stress can be applied before a material undergoes plastic deformation. Beyond this point, the material will not return to its original shape when the stress is removed, but will remain deformed or even break.
1.7227+QT Heat conductivity
At room temperature the heat conductivity for the 1.7227+QT is at 42,6 W/(m*K).
Wärmeleitfähigkeit
Wert W/(m*K)
Temperatur
XX
XX °C
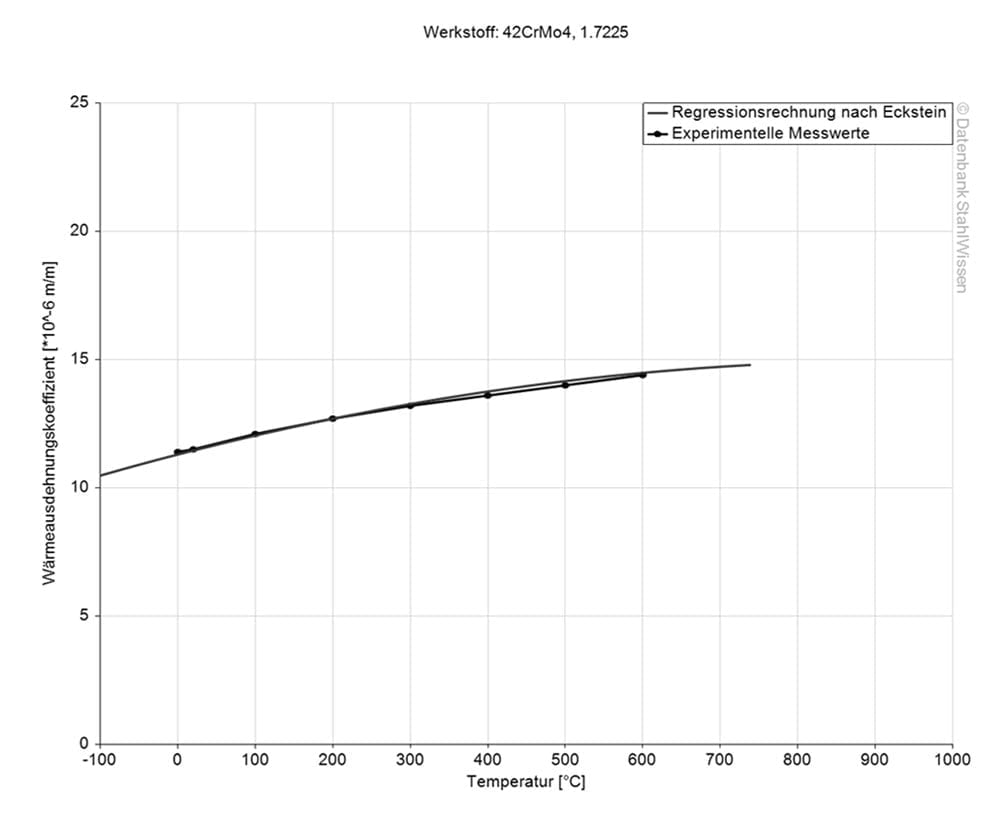
1.7227+QT Thermal expansion coefficient
The coefficient of thermal expansion indicates how much the material can expand or contract when the temperature changes. This is very important information, especially when working with high temperatures or when there are significant temperature fluctuations during use.
Medium thermal expansion coefficient
Value 10-6m/(m*K)
At a temeprature of
11.1
20 – 100 °C
12.1
20 – 200 °C
12.9
20 – 300 °C
13.5
20 – 400 °C
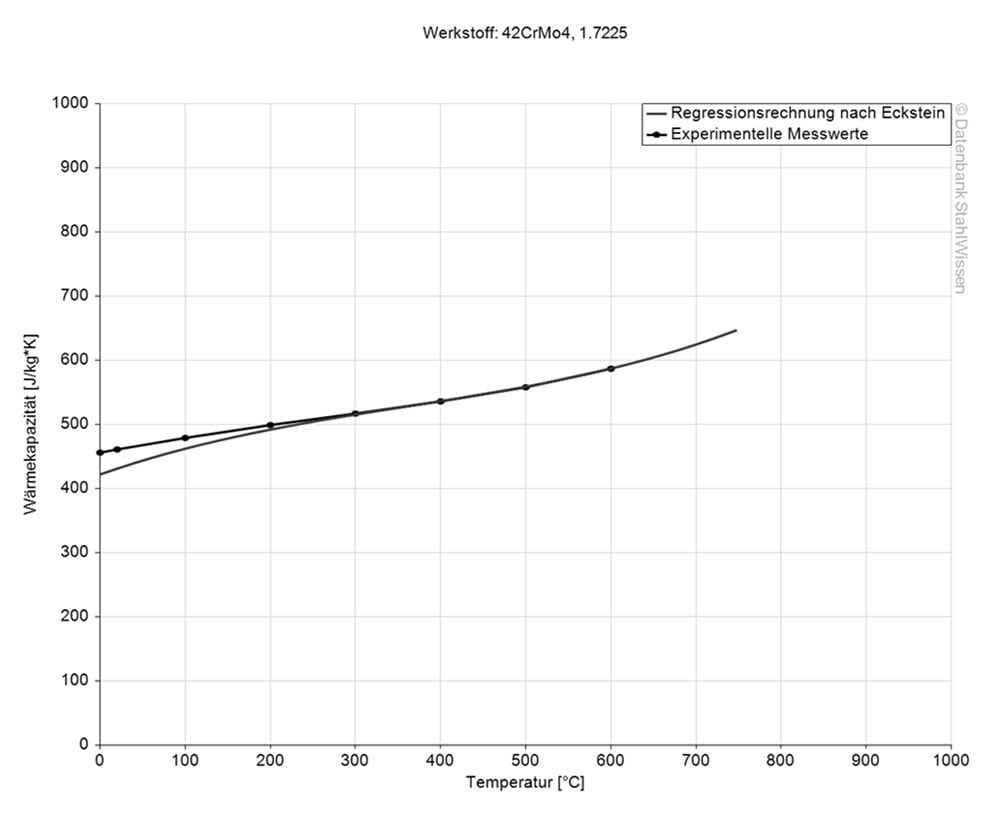
1.7227+QT Specific heat capacity
The value of the specific heat capacity shows how much heat is needed to heat a specific amount of material by 1 Kelvin.
1.7227+QT Specific electrical resistance
The following table shows the specific electrical resistance. Electrical conductivity is the reciprocal of electrical resistivity.
Table of the specific electrical resistivity
Value (Ohm*mm2)/m
At a temperature of
~ 0.19
~ 20 °C

PASSION!

1.7227+QT Procedure
1.7227+QT Heat treatment
The 1.7227+QT material can be heated to 860 °C and quenched in oil. The 1.7227+QT material can achieve a good range of properties through normalising and tempering.
1.7227+QT Annealing
Heat the workpieces evenly to a temperature 680 – 720 °C and follow this up with a slow cooling down in the furnace to reach a hardness of approx. 217 HB.
1.7227+QT Stress relieving
The 1.7227+QT should be heated to a temperture of 593 – 705 °C and held for 2 hours at that temperature. After it can be cooled down in air.
1.7227+QT Normailsing
This matrial grade can be normalised befor it is hardened. For that it is heated to a temperature of 840 – 880 °C and cooled in air after.
1.7227+QT Tempering
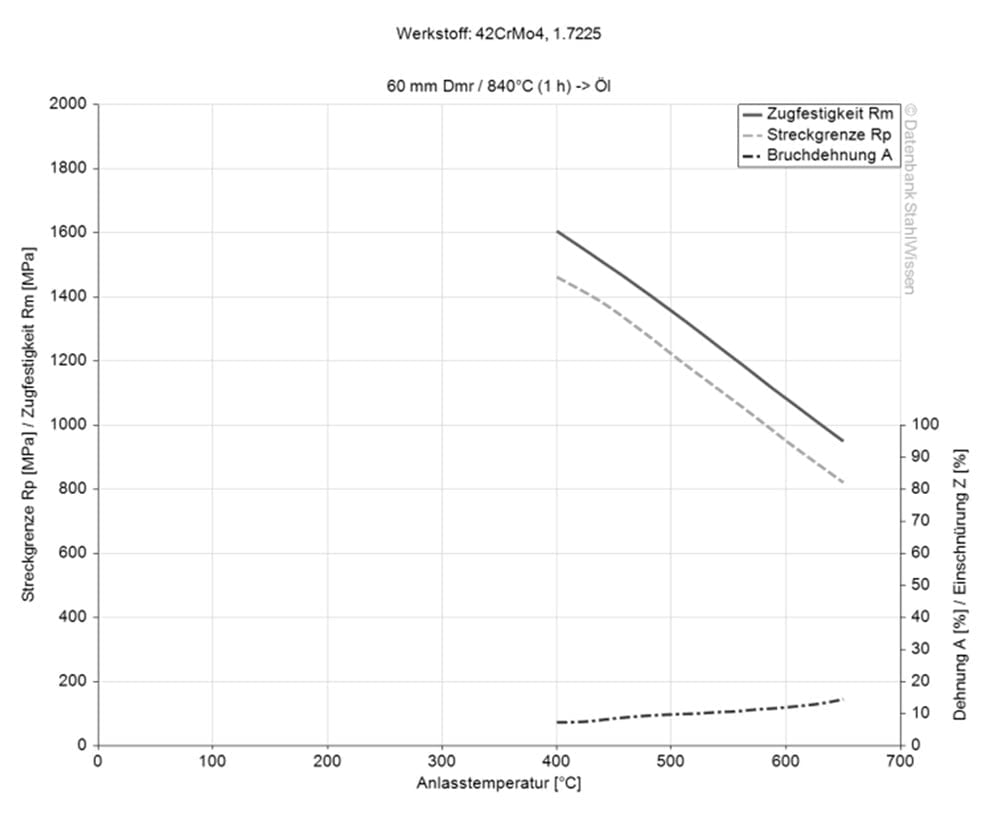
The higher the tempering temperature, the softer and more ductile the 1.7227+QT becomes. In general, hardness and ductility are determined by tempering the material. The higher the ductility, the lower the hardness, and vice versa. Apart from the advantage of giving the steel the desired and required properties, the material can be made stress-free, making it less prone to cracking and giving it better deformation behaviour due to tempering.
1.7227+QT Tempering temperature
The 1.7227+QT can be tempered at temperatures of 540 – 680 °C depending on hardness and needed propeties. After tempering the material should be cooled in air.
1.7227+QT Hardening
For hardening the 1.7227+QT should be heated slowly and evenly to 820 – 860 °C and after depending on size and complexity of the workpiece be quenched in water or oil. After quenching the possible working hardness is between 27 – 48 HRC.
1.7227+QT Quenching
The 1.7227+QT can be quenched in oil to room temperature and should be tempered straight away after.
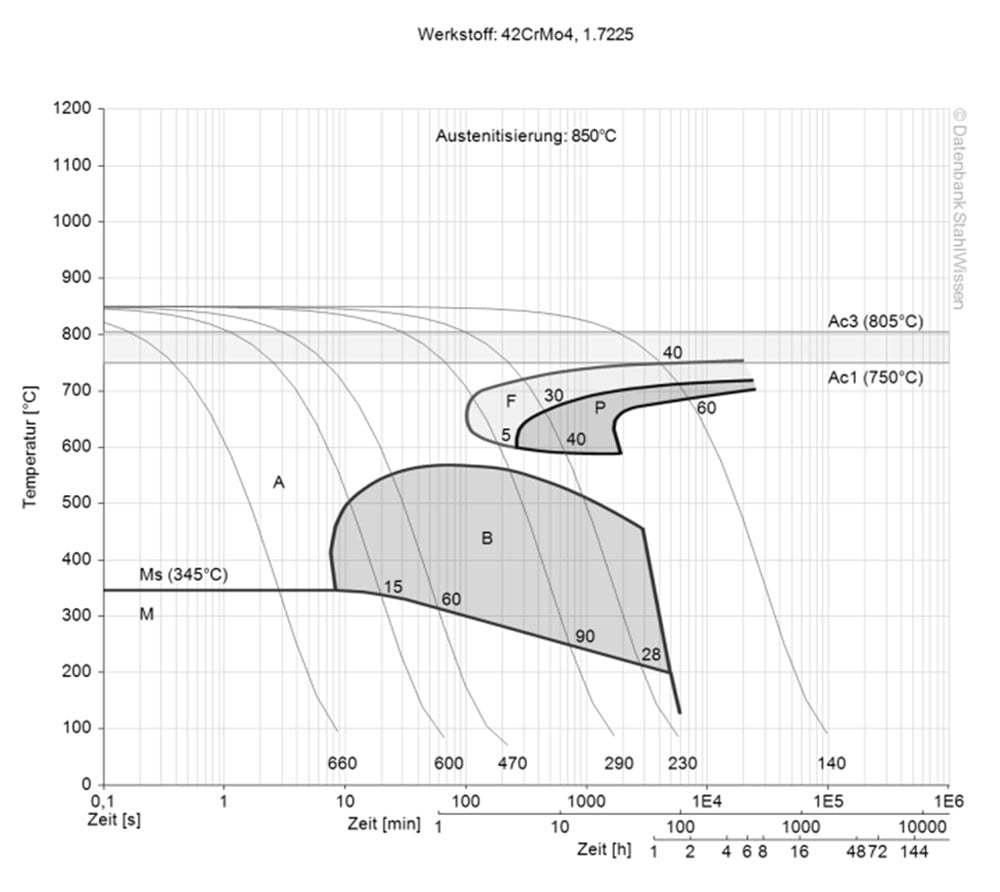
1.7227+QT Continous TTT-diagram
This diagram shows mirco changes over time at different temperatures. This can be important during heat treatment as it provides information about the optimal conditions for processes such as hardening, annealing and normalising.
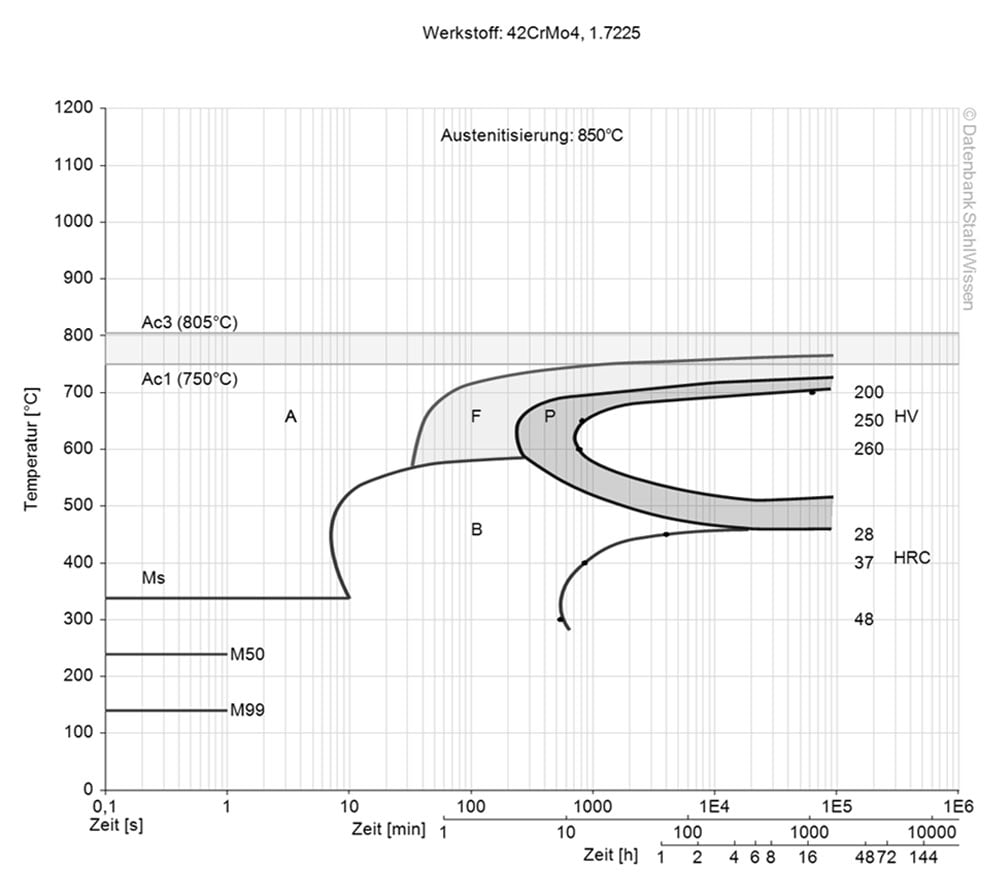
1.7227+QT Isothermal TTT-diagram
This diagram shows the structural changes at the micro level over time at a constant temperature. It shows at what temperature and after what time different phases, e.g. perlite, martensite or bainite, begin to form.
1.7227+QT Surface treatment
1.7227+QT Nitriding
The 1.7227+QT can be nitrided to give it a higher surface hardness. When nitriding nitrogen is diffused into the surface of the matrial to give it a harder surface and/or an improved corrosion resistance.
1.7227+QT Processing
After the heat treatment the 1.7227+QT has a microstructure needed for this material grade to be machined better.
1.7227+QT Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
It is possible to EDM this grade of steel in its annealed and hardened condition. After EDM, the recast layer, a thin white layer, should be removed by grinding and polishing for example, otherwise it may affect its service life and the performance of the workpieces.
1.7227+QT Forging
The 1.7227+QT can be forged in a temperature range of 900 – 1000 °C followed by a cooling down in still air or sand.