1.2083 ESR - AT A GLANCE
What kind of steel is the 1.2083 ESR?
Tool steel 1.2083 ESR (ESR = Electro-Slag-Refined or Remelted), a corrosion-resistant cold work steel, belonging to the plastic mold steels, with a high chromium content it has very good corrosion resistance (in its hardened condition) and good wear resistance.
The X40Cr14 ESR can easily be machined and is, due to the purity of the ESR material, highly polishable. With high compression strength and high wear resistance, the low-distortion through-hardener is suitable for injection molds of all types where good resistance to chemical aggressive molding compounds are required.
The remelting process provides this tool steel with a very low inclusion content, which makes it possible to provide a mirror finish when used for instance for lens molds or photoetching.
Properties
Steel grade 1.2083 ESR is a steel grade with good corrosion resistance, hardness and toughness that is easy to machine and responds well to heat treatment. This makes it ideal for a wide range of applications, such as industrial tools and medical instruments. Highly polished, it even finds its way into our households, for example for cutlery.
- High hardenabilty
- Good wear resistance
- Good machinability
- EDM machinable
- Etchable
- Excellent polishability
- Low distortion through-hardener
- Nitriding is not commonly done
- Conditionally acid resistant
Applications
The 1.2083 ESR can be used for applications that need corrosion or staining resistance, e.g., for molding of corrosive materials like PVC, acetates, for molds subjected to humid working conditions as well as surgical and dental instruments and tools.
Wear resistance, e.g., for molding abrasive materials and high surface finish, e.g., for the production of optical parts, such as lenses, for cameras and sunglasses, and for medical containers.
- Mechanical engineering
- Medical technology
- Plastic moulds
- Synthetic resin mould tools
- Die casting tools
- Light metal die casting
- Cutting tools
- Machine knives
- Kitchen knives
- Razors
- Shears
- Scraper blades
- Surgical instruments
- Measuring tools
- Roller bearings
- Ball bearings
- Ice-skates
- Pump parts
- Valves
1.2083 ESU Standard values
Chemical composition:
| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.36 - 0.42 | 0.0 - 1.0 | 0.0 - 1.0 | 0.0 - 0.03 | 0.0 - 0.03 | 12.5 - 14.5 |
Chemical designation:
X40Cr14
Working hardness:
50-55 HRC
Delivery condition:
max. 241 HB
1.2083 ESR Physical properties
What group of steel does the 1.2083 ESR belong to?
- Tool steel
- Stainless steel
- Cold work steel
- Plastic mould steel
Why ESR material?
Electro-Slag-Remelted or ESR is a process where steel is remelted and passes through slag which removes debris and impurities from the steel.
What is left is steel with a higher cleanliness and a finer, more homogeneous microstructure. Reducing the impurities from steel gives the steel an overall integrity with fewer weak spots.
ESR steel can exhibit better mechanical properties like higher tensile strength, yield strength, toughness, wear resistance, better surface finishes, longer tool life.
Here the already existing corrosion resistance of the 1.2083 ESR is being improved even further through the ESR process due to the reduction of inclusions and other imputities.
Is the 1.2083 ESR a stainless steel?
Yes, the 1.2083 ESR can be classified as a stainless steel as it containes 12,5 – 14,5% chromium. To be classified as a stainless steel the material has to contain a minimum mass fraction of 10,5% of chromium.
Is the 1.2083 ESR corrosion resistant?
With a mass fraktion of 12,5 – 14,5% of chromium the 1.2083 ESR is corrosion resistant.
1.2083 ESR general corrosion resistance
The 1.2083 ESR is corrosion resistant in water, steam, mildely organic acids, diluted solutions of nitrates, carbonates and other salts.
Is the 1.2083 ESR magnetisable?
Yes the 1.2083 ESR is magnetisable and even more so in its hardened state than in its annealed state. The magnetic properties make it possible to use magnetic clamping plates to machine this material.
1.2083 ESR Cold work
Cold forming of 1.2083 ESR must be carried out carefully to prevent cracking. Cold working of this material can increase its hardness and strength.
1.2083 ESR Wear resistance
On a scale where 1 is low and 6 is high the 1.2083 ESR recieves a 4 for its wear resistance.
1.2083 ESR Technical properties
Is tool steel 1.2083 ESR a knife steel?
Yes, the 1.2083 ESR can be used to manufacture knives which is due to its toughness, corrosion resistance and edge retention. Although this material grade has good corrosion resistance, regular maintenance, cleaning and drying can give knives made from this steel a longer service life.
1.2083 ESR Working hardness
The working hardeness for tool steel 1.2083 ESR is in the range of 50 – 55 HRC.
1.2083 ESR Density
At a temperature of 20°C the density for steel grade 1.2083 ESR is at 7,8 g/cm³.
1.2083 ESR Tensile strength
On delivery the 1.2083 ESR has a tensile strength of approx. 815 N/mm2. For this result the material is undergoing a tensile test which shows how much force is needed before the material starts to stretch or elongate before it breaks.
1.2083 ESR Yield strength
The yield strength indicates how much stress can be applied before a material undergoes plastic deformation. Beyond this point, the material no longer returns to its original shape when the stresses are removed, but remains deformed or even breaks.
The range for this tool steel is at 1600 N/mm2.
1.2083 ESR Machinability
For its machinability the 1.2083 ESR recieves a 4 on a scale where 1 is low and 6 is high.
1.2083 ESR Heat conductivity
For the 1.2083 ESR the heat conductivity at a temperature of 23°C is at 22,6 W/(m*K).
Heat conductivity
Value W/(m*K)
At a temperature of
22.6
23 °C
24.0
150 °C
24.6
300 °C
24.9
350 °C
24.4
400 °C
23.7
500 °C
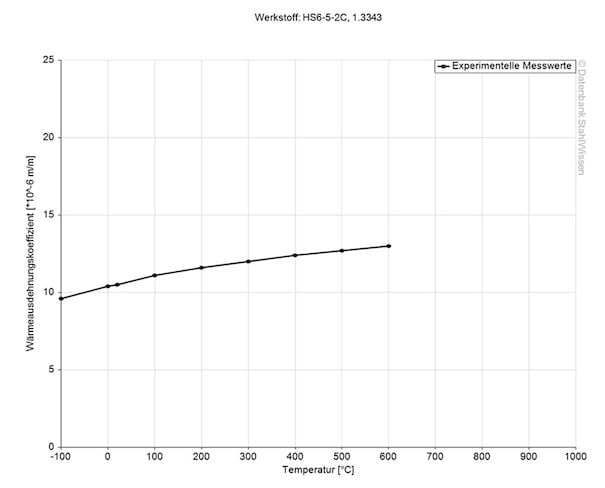
1.2083 ESR Thermal expansion coefficient
The thermal expansion coefficient shows how much a material expands or contracts at any temperature changes. This information can be relevant when when components or parts are exposed to high temperatures or for applications with ever changing temperatures.
Medium thermal expansion coefficient
Value 10-6m/(m*K)
At a temperature of
11.1
20 – 100 °C
11.6
20 – 200 °C
12.0
20 – 300 °C
12.3
20 – 350 °C
12.4
20 – 400 °C
12.5
20 – 450 °C
12.6
20 – 500 °C
1.2083 ESR Specific heat capacity
The specific heat capacity of tool steel 1.2083 ESR at room temperature is 0,46 J/kg*K. This value shows how much heat is needed to heat a specific amount of material by 1 Kelvin.
1.2083 ESR Specific electrical resistance
The following table shows the specific electrical resistance. Electrical conductivity is the reciprocal of electrical resistivity.
Value (Ohm*mm²)/m
Bei einer Temperatur von
0.6
20 °C
Table of the specific electrical resistivity

THAT IS OUR €co-Präz®!

1.2083 ESR Procedure
1.2083 ESR Heat treatment
The heat treatment determines the material properties and should be carried out with care. Properties such as strength, toughness, surface hardness and temperature resistance are determined, which in turn can extend/improve the service life of parts, tools and components.
Heat treatment includes solution heat treatment, soft annealing, normalising, stress-relief heat treatment, but also tempering, hardening and quenching.
1.2083 ESR Annealing
The material has to be heated evenly to a temperature of 890 °C. After that it is cooled back down in the oven to 650 °C and the cooling down to ambient temperature can be done in air.
1.2083 ESR Stress relieving
After the 1.2083 has been machined it is heated evenly to a temperature of 650 °C in which it is held for 2 hours. Then it gets cooled down in the oven to a temperature of 500 °C and can then cool down further in air.
1.2083 ESR Annealing
Select the desired tempering temperature, temper the material twice and cool it to room temperature between the first and second tempering.
The tempering temperature should not fall below 250 °C and should be maintained at the selected temperature for at least 2 hours. A temperature of 250 °C is recommended to achieve the best combination of hardness, toughness and corrosion resistance.
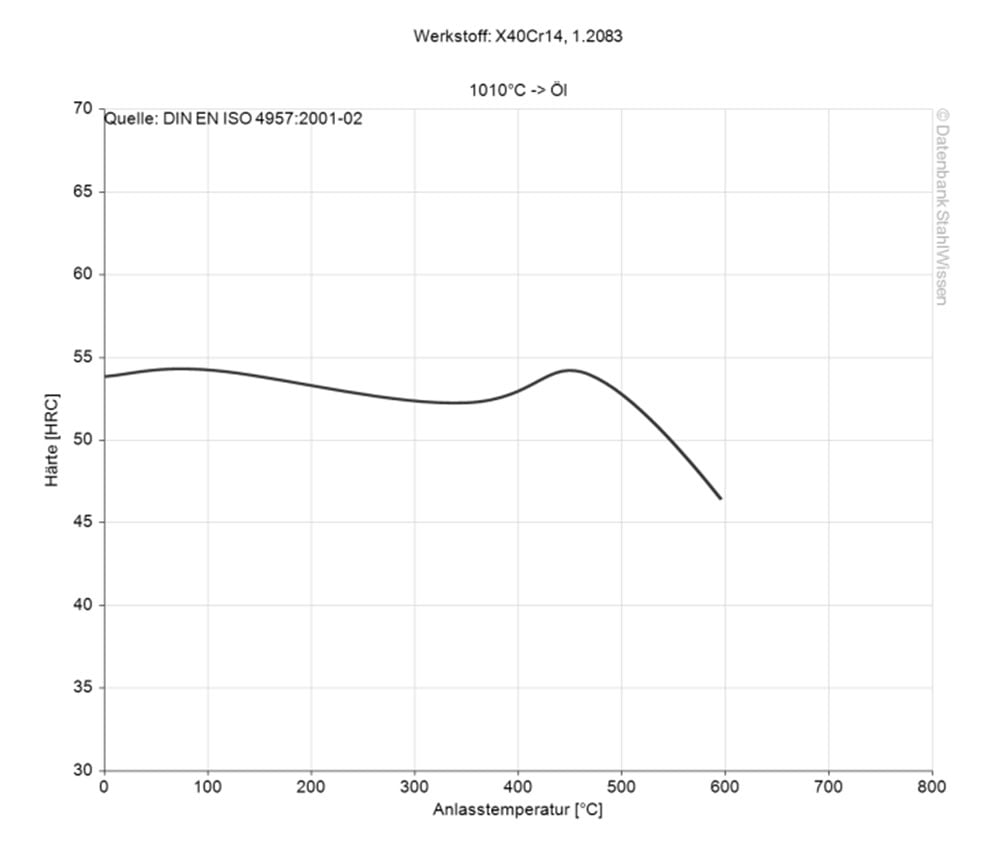
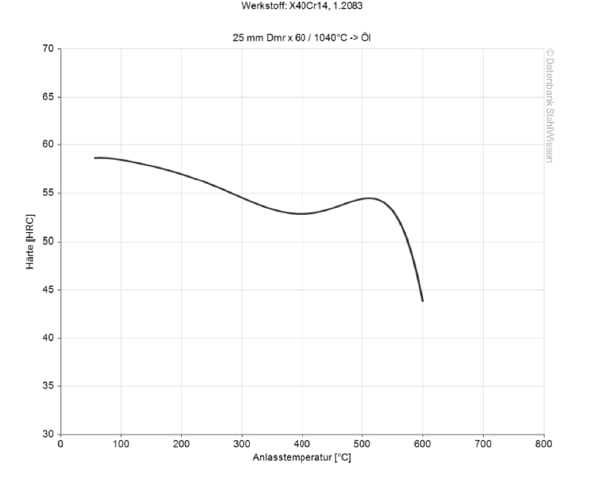
1.2083 ESR Hardening
Pre-heat the material to a temperature of 600 – 850 °C.
For austenising, the 1.2083 ESR material is heated to a temperature of 1010 – 1067 °C.
1.2083 ESR Sub-zero treatment
Cryogenic treatment of the 1.2083 ESR can convert residual austenite into martensite and improve properties such as the dimensional stability of this material.
1.2083 ESR Quenching
Quenching should be done as quick as possible to get the desired properties. Still a good balance of the cooling speed is needed that the material does not deform or crack.
When the parts are cooled down to a temperature of 50 – 70 °C they should be tempered.
- Fluidised bed or salt bath at 250–550 °C, followed by cooling in an air stream
- Vacuum, with suffcient positive pressure
- Warm oil, approx. 80 °C
1.2083 ESR Continuous TTT-Diagram
The TTT-diagram usually shows micro-changes over time at different temperature . These are important in heat treatment as they provide information on the optimal conditions for processes such as hardening, annealing and normalising.
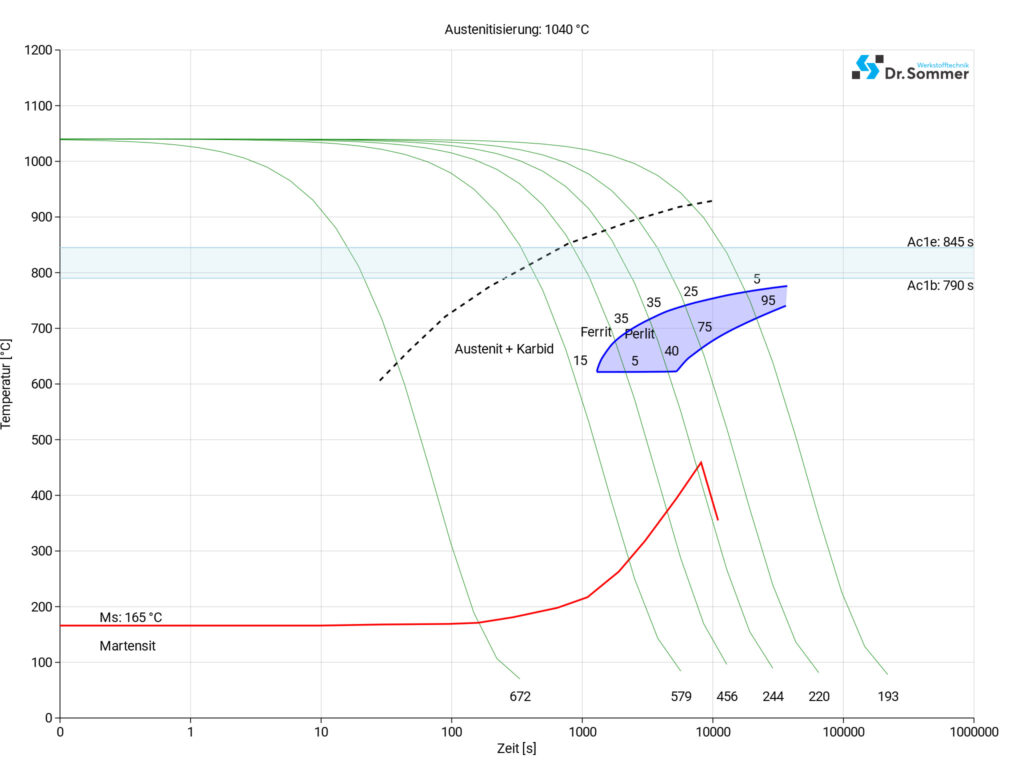
1.2083 ESR Surface treatment
1.2083 ESR Passivation
Passivation involves removing free iron from the surface by treating it with an acid solution, such as citric or nitric acid. Passivation creates a protective oxide layer that increases the corrosion resistance of this material.
1.2083 ESR Polishing
1.2083 ESR tool steel can be polished to an excellent surface finish. Polishing reduces friction, improves surface quality and enhances the aesthetic appearance.
1.2083 ESR Plastic mold steel PVD and CVD coating
In PVD and CVD coating, a hard layer, e.g. TiN (titanium nitride), is applied to improve the wear resistance and hardness of the material.
- PVD – physical vapour deposition
- CVD – chemical vapour deposition
1.2083 ESR Electroplating
In this process, a layer of metal, such as nickel or chrome, is applied to the metal surface to make it more resistant to corrosion, to reduce friction or achieve a decorative effect.
1.2083 ESR Texturing
Texturing creates a pattern on the surface of the material that serves aesthetic purposes but can also be functional, for example to retain lubricants, improve the grip of the workpiece or enhance electrical and thermal conductivity.
1.2083 ESR Processing
1.2083 ESR Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
As this is a hard material, conventional machining methods can be challenging and lead to excessive tool wear. Since there is no direct contact with the material during eroding, tool wear is not a problem in itself, although electrodes must be replaced regularly. Erosion is often used for hard materials, complex shapes, tight tolerances and a good surface finish on parts.
1.2083 ESR Dimensional changes
As with all metals, 1.2083 ESR can expand when heated and contract when cooled. Phase changes can also lead to dimensional changes, depending on temperature, type of equipment and cooling media used during hardening and tempering, dimensional changes may vary.
1.2083 ESR Welding
Welding should be avoided as far as possible due to the high risk of cracking.
If welding is unavoidable, heat the material to 200–250 °C and maintain this temperature to prevent cracking. After welding, temper the hardened material at 10–20 °C below the original tempering temperature. Soft-annealed material should be heated evenly to 890 °C in a protected atmosphere. Then cool in the furnace at 20 °C per hour to 850 °C and then at 10 °C per hour to 700 °C. From there, the material can be further cooled in air.
Welding consumables with the same composition as the base metal should be used.
1.2083 ESR Photo Etching
Thanks to the ESR process, 1.2083 ESR has very few inclusions and is therefore suitable for photo etching.