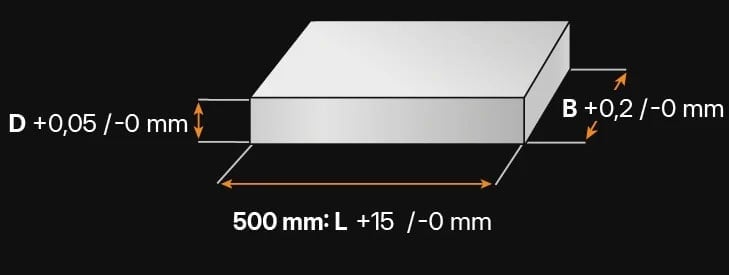
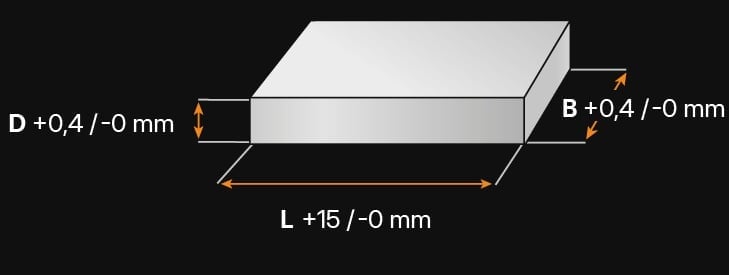
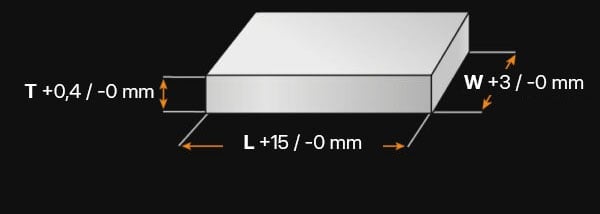
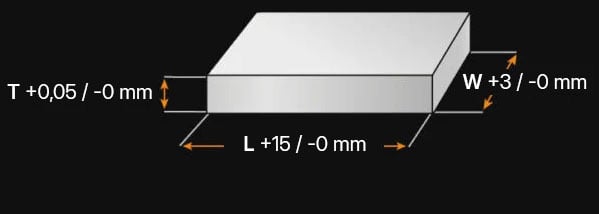
1.2294 - AT A GLANCE
What kind of steel is the 1.2294?
Teh 1.2294 (~X5CrS12) is a pre-hardened, corrosion resistant plastic mould steel which is easily machined and magnetisable. Due to its low carbon content this steel grade is easy to weld. It has a good resistance to agressive plastics as well as humid conditions. Further heat treatent is not intended for this tool steel grade.
Properties
The 1.2294 is a versatile and high performance steel which can be used for mechanical engineering as well as in the autootive industry, for water valves and surgical instruments.
- Tool steel
- Plastic mould steel
- Corrosion resistant
- Pre-hardened
- Magnetisable
- Very good machinability
- Good toughness
- Good weldability
- Resistant against agressiv plastics
- Resistant in humid conditions
- No further heat treatment is intended
Applications
The tool steel 1.2294 is pre-hardened and corrosion resistant plastic mould steel which resistant to agressive plastic moulds and can be used in many differnet industries and applications.
- Mechanical engineering
- Apparatus engineering
- Plastic processing
- Injection tools
- Base Plates
- Assembling parts
- Moulding frames
- Plastic moulds
- Extrusion tools
- Valves
- Steam valves
- Water valves
- Fittings parts
- Pump construction
- Pump rods
- Compressor construction
- Compressor parts
- Surgical instruments
1.2294 Standard values
Chemical composition: (+additives):
| C | Mn | S | Cr |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.05 - 0.05 | 1.3 - 1.3 | 0.15 - 0.15 | 12.5 - 12.5 |
Chemical designation:
~X5CrS12
Working hardness:
approx. 33 HRC (reference value for delivery condition)
Delivery condition:
max. 330 HB
1.2294 Physical properties
What group of steel does the 1.2294 belong to?
- Tool steel
- Plastic mould steel
- Stainless steel, corrosion resistant
Is the 1.2294 a stainless steel?
To be classified as a stainless steel a material has to have a mass fraction of 10,5 % chromium. This means that the 1.2294 could be classified as a stainless steel as it contains 12,5 % chromium.
Is the 1.2294 corrosion resistant?
With a mass fraction of 12,5 % chromium the 1.2294 is corrosion resistant.
1.2294 General corrosion resistance
As a corrosion resistant mould steel the 1.2294 can be used for aggresive plastics, in humid climatic conditions and in buildings where there is a condensation build-up.
Is the 1.2294 magnetisable?
The 1.2294 has a ferro magnetic structur which makes it magnetisable which makes it possible to use magnetic clamping plates to machine this material.
1.2294 Wear resistance
On a scale where 1 is low and 6 is high the 1.2294 receives a 2 for its wear resistance.
1.2294 Technical properties
1.2294 Working hardness
At delivery the 1.2294 has a working hardness of approx. 33 HRC.
1.2294 Density
At room temperature the tool steel 1.2294 has a density of 7,7 g/cm³.
1.2294 Tensile strength
The tensile strength for the tool steel 1.2294 is at approx. 1125 N/mm2. To reach this result the material undergoes a tensile test to show how much stress is needed before the material starts to elongate before it breaks.
1.2294 Machinability
On a scale where 1 is low and 6 is high the 1.2294 receives a 6 for its machinability.
1.2294 Heat conductivity
The following table shows the heat conductivity for the tool steel 1.2294 at different temperatures.
Heat conductivity
Value W/(m*k)
At a temperature of
24.6
23 °C
25.7
150 °C
58.8
300 °C
25.7
350 °C
25.4
400 °C
24.7
500 °C
1.2294 Thermal expansion coefficient
The following table shows the expansion or contraction at different temperatures. This can be very improtant when working with high or ever changing temperatures.
Medium thermal expansion coefficient
Value 10-6m/(m*K)
At a temperature of
10.3
20 – 100 °C
10.9
20 – 200 °C
11.2
20 – 300 °C
11.4
20 – 350 °C
11.6
20 – 400 °C
11.8
20 – 450 °C
12.0
20 – 500 °C
1.2294 Specific heat capacity
At room temperature the specific heat capacity of the 1.2294 is at 0,46 J/kg*K. This value shows how much heat is needed to heat a specific amount of material by 1 Kelvin.

CORROSION RESISTANT STEEL!

1.2294 Procedure
A further heat treatment for this tool steel is not intended.
1.2294 Surface treatment
In general, the choice of surface treatment depends on the requirements, the environment in which the workpieces/tools are used, the required properties and the expected loads. Polishing can be a type of surface treatment that increases corrosion resistance but also has an attractive effect.
1.2294 Processing
1.2294 Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
In general, a material is eroded to produce workpieces from a single piece. Erosion can be used to produce dies or more complex shapes. There are various methods of eroding different materials, such as wire erosion, spark erosion or sinker erosion.
1.2294 Machining allowance / dimensional changes
Dimensional changes may occur in material 1.2294 during heat treatment in the form of warping or dimensional changes caused by internal stresses. During cooling, care should be taken to cool the material evenly, as otherwise it may warp. To avoid dimensional changes, precise heat treatment and machining should be carried out and stresses should be relieved.
1.2294 Forging
For forging, the 1.2294 material is heated evenly to a temperature of 950–1050 °C and forged. The forging temperature should not fall below 900 °C to prevent cracking. After forging, the workpiece is slowly cooled in the furnace or wrapped in insulating material. Slow cooling prevents the build-up of internal stresses and crack formation.
A subsequent heat treatment to relieve residual stresses is recommended in order to improve dimensional stability and also to improve its mechanical properties.
1.2294 Welding
With the appropriate precautions, preparations, processes and parameters, 1.2294 can be welded. The material should be thoroughly cleaned beforehand. The material is preheated before welding to prevent stresses and cracking. With the right choice of welding process and the appropriate parameters, a good and durable weld can be achieved. Finally, heat treatment is applied to reduce any remaining stresses and restore uniform mechanical properties.