1.4418 - AT A GLANCE
What kind of steel is the 1.4418?
The steel grade 1.4418 is a martensitic, prehardened chromium-nickel-molybdenum steel. It has high strength, good toughness and good corrosion resistance, even in aggressive media such as acids.
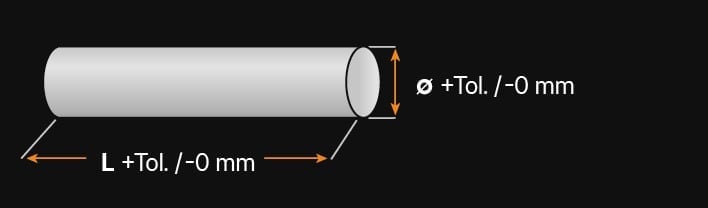
1.4418 is cold formable, weldable and forgeable. In its tempered state, this material has good mechanical properties, making it suitable for use in the gas and oil industry. This material is cold formable and has an operating temperature between -30 and 300°C.
Properties
With a good combination of hardness, toughness and corrosion resistance the 1.4418 can be used for applications where high mechanical stresses or various types of corrosion like pitting or crevice corrosion, pose a risk.
- Martensitic stainless steel
- Chromium-Nickel-Molybdenum-Steel
- Corrosion resistant
- Acid resistant
- Polishable
- Weldable
- Can be used for temperatures between -30 to 300°C
- Cold working
- Cold heading is not common
Applications
As a pre-hardened stainless steel with an outstanding combination of high strength properties, good toughness and very good corrosion resistance the 1.4418 can be used in many industries and applications.
- Automotive industry
- Chemical industry
- Aviation and space industry
- General engineering
- Plant engineering
- Shipbuilding
- Shafts
- Axes
- Environmental technology
- Centrifuge components
- Pump components
- Energy technic
- On- and Offshore
1.4418 Standard values
Chemical composition:
| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Mo | Ni | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 - 0.06 | 0.0 - 0.7 | 0.0 - 1.5 | 0.0 - 0.04 | 0.0 - 0.03 | 15.0 - 17.0 | 0.8 - 1.5 | 4.0 - 6.0 | ≥ - 0.02 |
Chemical designation:
X4CrNiMo16-5-1
Working hardness:
approx. 34 HRC (delivery condition) up to 39 HRC
Delivery condition:
max. 323 HB
1.4418 Physical properties
What group of steel does the 1.4418 belong to?
- Martensitic stainless steel
- Stainless steel, corrosion resistant
- Stainless steel, acid resistant
- Stainless steel
- Cold work steel
Is the 1.4418 a stainless steel?
To be classified as a stainless steel it has to have a mass fraction of at least 10,5 % of chromium. With a mass fraction of 15 – 17 % the 1.4418 is a stainless steel.
Is the 1.4418 corrosion resistant?
Yes, with a mass fraction of 15 – 17 % the 1.4418 fullfills the minimum of 10,5 % of chromium and is corrosion resistant.
1.4418 General corrosion resistance
With its chemical composition, 1.4418 is resistant to various types of corrosion and can be further improved by polishing.
This steel grade is insensitive to intergranular corrosion and resistant to fatigue and stress corrosion cracking.
The combination of chromium, nickel and molybdenum forms a stable passive layer on the workpieces, which protects them from corrosion and remains intact even under high loads and in various environments.
Intergranular corrosion of 1.4418
Its low carbon content reduces the formation of chromium carbides at the grain boundaries, making 1.4418 less susceptible to intergranular corrosion.
1.4418 Stress corrosion
The addition of 4–6% nickel and suitable heat treatment can reduce susceptibility to stress corrosion cracking.
1.4418 Crevice corrosion
The added molybdenum promotes the formation of the passive layer and thus prevents the development of crevice corrosion.
1.4418 Pitting
With a chromium content of 15–17% and a molybdenum content of 0.8–1.5%, the material has improved resistance to pitting, especially in chloride-containing environments.
Is the 1.4418 magnetisable?
As a martensitic stainless steel the 1.4418 can be magnetised and magnetic clamping for machining is possible.
1.4418 Wear resistance
On a scale where 6 is high and 1 is low the 1.4418 receives a 4 for its wear resistance.
1.4418 Technical properties
Is the 1.4418 a knife steel?
Although the 1.4418 has properties that are suitable for knives, such as corrosion resistance and toughness, its hardness is not high enough and the cutting edge dulls more quickly than with a suitable knife steel. The appropriate knife steel has a good combination of hardness and sharpness and retains its cutting edge for a long time. Therefore, a different steel should be used for knives.
1.4418 Working hardness
At delivery the working hardness for the 1.4418 is in the range of 34 – 39 HRC.
1.4418 Density
At room temperature the denity for the 1.4418 is at 7,7 g/cm3.
1.4418 Tensile strength
The 1.4418 has a tensile strength of approx. 1095 N/mm2. This value is the result of a tensile test that shows how much force is required before the material begins to stretch or deform before it breaks.
1.4418 Yield strength
The yield strength indicates how much stress can be exerted on a material before it undergoes plastic deformation. Beyond this point, it will not return to its original shape, even if the stress is removed. The material will deform permanently or break beyond this point.
The yield strength for 1.4418 stainless steel is at 550 N/mm2.
1.4418 Machinability
On a scale where 1 is low and 6 is high the 1.4418 receives a 3 for its machinability.
1.4418 Temperature resistance
Stainless steel 1.4418 can be used at a temperature range of -30 °C up to 300 °C.
1.4418 Heat conductivity
The heat conductivity of stainless steel 1.4418 at room temperature is at 15,0 W/(m*K).
1.4418 Thermal expansion coefficient
The coefficient of thermal expansion indicates how much the material can expand or contract when the temperature changes. This is very important information, especially when working with high temperatures or when there are significant temperature fluctuations during use.
Medium thermal expansion coefficient
Value 10-6m/(m*K) Wert
At a temperature of
10.3
20 – 100 °C
10.8
20 – 200 °C
11.2
20 – 300 °C
11.6
20 – 400 °C
1.4418 Specific heat capacity
The specific heat capacity for stainless steel 1.4418 at room temperature is 0,43 J/kg*K. This value indicates how much heat is required to heat a certain amount of material by 1 Kelvin.
1.4418 Specific electrical resistance
The specific electrical resistance for stainless steel 1.4418 can be found in the following table. Electrical conductivity is the reciprocal of specific resistance.
Specific electrical resistance
Value (Ohm*mm²)/m
At a temperature of
~ 0.8
~ 20 °C

365 DAYS A YEAR – WE ARE HERE FOR YOU – VISIT OUR ONLINE SHOP AT WWW.PREMIUM-STEEL.CO.UK/SHOP
1.4418 Procedure
1.4418 Heat treatment
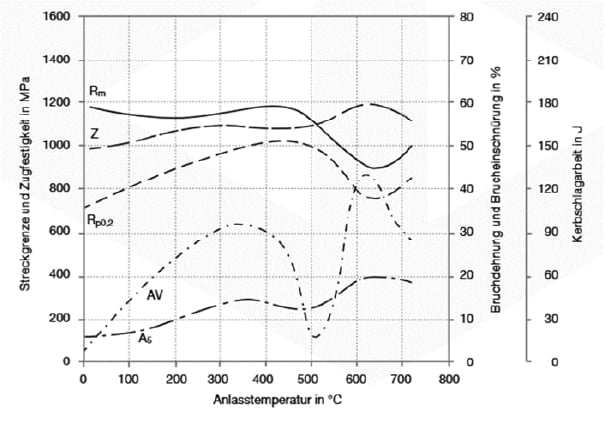
Heat treatment is used to determine material properties. It should therefore always be carried out with care. Properties such as strength, toughness, surface hardness and temperature resistance are determined, which in turn can extend/improve the service life of parts, tools and components.
Heat treatment includes solution annealing, soft annealing, normalising, stress relief annealing, but also tempering, hardening and quenching or tempering.
1.4418 Soft annealing
To soft anneal the 1.4418 heat it to a temperature of 600 – 650 °C and hold it for approx. 4 hours. Then let the material cool down in air or the furnace.
1.4418 Tempering
For tempering heat the 1.4418 to a temperature of 550 – 620 °C and afterwards let it cool down slowly in either the furnace or in air.
1.4418 Hardening
To harden the 1.4418 it is heated evenly to a temperature of 950 – 1050 °C and followed up by quenching.
1.4418 Quenching
Stainless steel 1.4418 can be quenched in the following media:
- Polymer
- Oil
- Air
1.4418 Surface treatment
1.4418 Nitriding
During the nitriding process nitrogen is diffused into the surface of the 1.4418. This gives the material a hard nitride layer for improved wear resistance.
1.4418 Passivation
Passivation involves removing free iron from the surface by treating it with an acid solution, such as citric or nitric acid. Passivation creates a protective oxide layer that increases the corrosion resistance of this material.
1.4418 Electro polishing
During this process an electric current is used to remove a very thin layer of material which leaves a smooth and shiny surface. This is a non-mechanical process and is not to be confused with passivation which does not use an electric current.
1.4418 Polishing
In addition to an aesthetic finish a high gloss polishing can improve the corrosion resistance of the material as well as minimising the adhesion of contaminants which is very important if parts are used in the food industry for example.
1.4418 PVD coating
In PVD (physical vapour deposition) treatment, a thin layer is applied to the surface of the material. This treatment can give the steel a unique colour and improve its surface properties.
1.4418 Processing
1.4418 Forging
The 1.4418 is preheated evenly to a temperature of 800 °C and then quickly to its forging temperature of 1050 – 1080 °C. During forging the temperature should not drop below 950 °C. For cooling the forging down again it should cool slowly in the furnace or dry ash.
1.4418 Welding
The material 1.4418 is preheated to a temperature range of 100 – 200 °C for welding. Welding consumables should be similar to the base material. Post-weld treatment consisting of annealing or tempering should be applied in order to bring the mechanical properties in the weld seam back into line with those of the base material, preventing the formation of cracks in the heat-affected zone.